Table Of Contents
Tripartite Evolutionary Game Analysis of Collaborative Governance in Construction and Demolition Waste Management
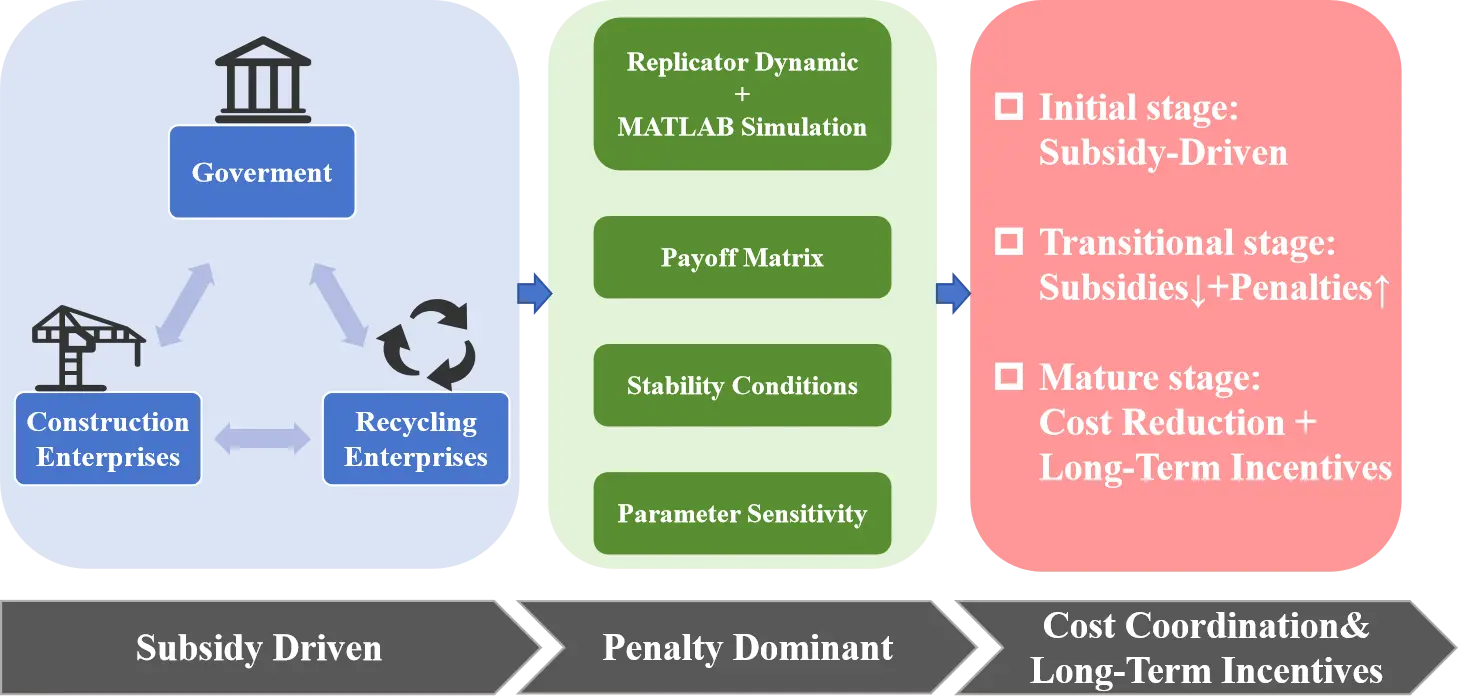
Construction and demolition waste management remains a critical challenge in China, where low recycling rates and fragmented stakeholder coordination impede the transition toward a circular economy. This study develops a tripartite evolutionary game ...
More.Construction and demolition waste management remains a critical challenge in China, where low recycling rates and fragmented stakeholder coordination impede the transition toward a circular economy. This study develops a tripartite evolutionary game model involving government regulators, construction enterprises, and recycling enterprises. By integrating replicator dynamics with MATLAB-based simulations and incorporating phased subsidies, penalties, and firm-level cost parameters, the model analyzes the strategic evolution of stakeholder behaviors. Simulation results show that a stable cooperative equilibrium emerges when subsidies for construction and recycling enterprises are set at E1 = 50 and E2 = 48, and the penalty H is at least 50. Under these conditions, the probability of adopting proactive strategies exceeds 0.9 within 50 iterations. While penalties remain consistently effective across all levels of market maturity, the marginal utility of subsidies declines sharply as the resource utilization rate (q) approaches 0.5. Increasing the initial cooperation probability of construction enterprises from 0.5 to 0.8 reduces convergence time by approximately 35%. High sorting costs (F > 45) and low resale revenues (I < 40) are identified as key barriers to sustained cooperation. Based on these findings, a three-phase policy strategy is proposed: subsidies should be deployed in the early stage to lower entry barriers; penalties should be prioritized during the transition phase; and transaction cost reduction and long-term revenue mechanisms should be emphasized in the mature stage. The study provides both theoretical and practical insights into sustainable governance of construction and demolition waste.
Less.Caimiao Zheng, ... Leins Wang
DOI:https://doi.org/10.70401/jbde.2025.0011 - June 26, 2025
Indoor Environmental Quality in an Occupied Whole Life Straw Bale House in England, UK
In response to policy and legislative measures targeting the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions, building design has increasingly prioritised airtightness and energy efficiency. However, existing literature raises concerns that such designs may lead ...
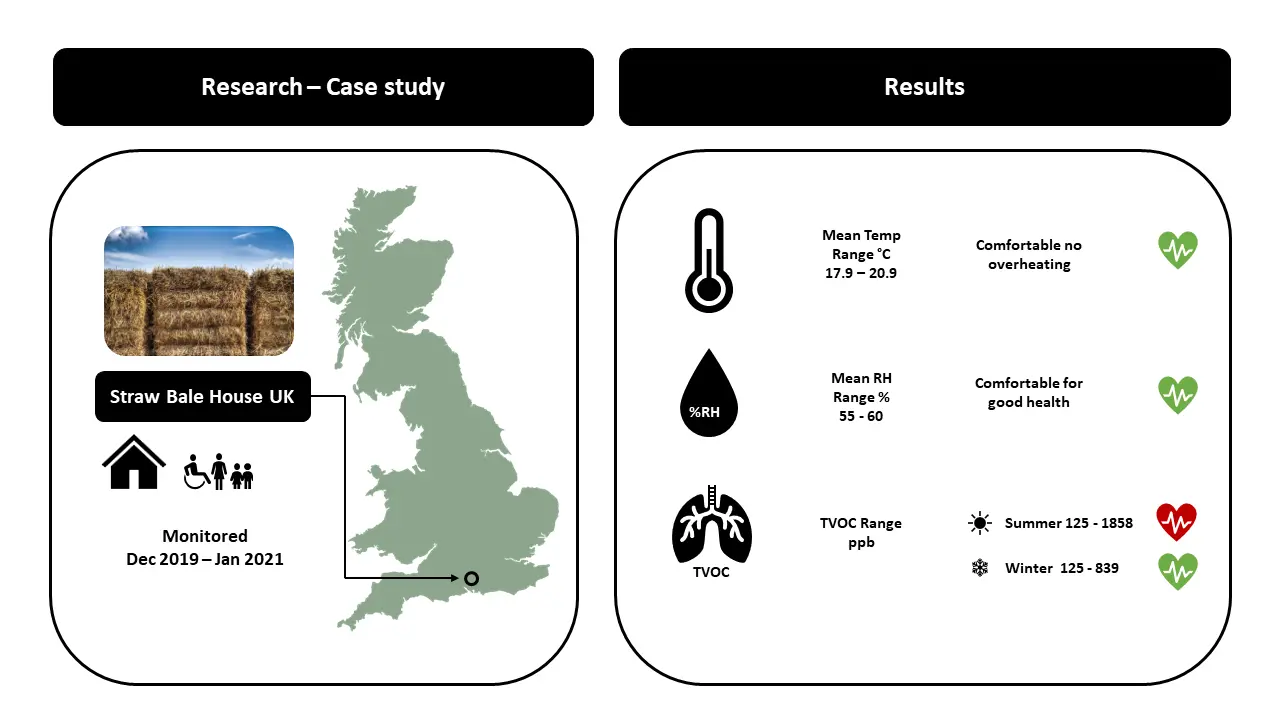
More.In response to policy and legislative measures targeting the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions, building design has increasingly prioritised airtightness and energy efficiency. However, existing literature raises concerns that such designs may lead to issues such as overheating and inadequate ventilation. At the same time, some designers have turned to low-carbon construction materials such as straw bales, not only to minimise embodied carbon emissions but also to promote occupant health. Although straw bale buildings are known for their thermal efficiency, limited data are available on their indoor environmental quality (IEQ) during occupancy. This study presents a case study evaluating the environmental performance of an airtight, energy-efficient straw bale dwelling equipped with a decentralised ventilation system, located in southern England, UK. The research investigates whether the home maintains thermal comfort throughout the year, with a focus on both summer and winter seasons, along with an assessment of relative humidity and total volatile organic compounds (TVOCs). Data were collected over a 14-month period and evaluated against established IEQ benchmarks. Findings revealed no instances of overheating, even during a summer heatwave; however, elevated TVOC concentrations were recorded in summer compared to winter. Indoor temperature results also differed from those reported in previous studies on UK airtight homes, underscoring the need for broader research into the IEQ performance of dwellings constructed with natural materials to determine the extent to which sustainable building practices contribute to occupant comfort.
Less.Janice A. Foster, Filbert Musau
DOI:https://doi.org/10.70401/jbde.2025.0010 - June 20, 2025
Causation analysis of crane-related accident reports by utilizing ChatGPT and complex networks
This study integrates ChatGPT and complex network (CN) techniques into an accident analysis framework designed to reduce manual effort in accident causation analysis. The proposed framework supports construction stakeholders in extracting causal factors ...
More.This study integrates ChatGPT and complex network (CN) techniques into an accident analysis framework designed to reduce manual effort in accident causation analysis. The proposed framework supports construction stakeholders in extracting causal factors (CFs) from accident reports and identifying both critical CFs and key causal paths. A multistep research design was adopted to develop and validate this novel framework for analyzing crane-related construction accident reports using ChatGPT and CN techniques. First, ChatGPT was prompted to extract CFs from a database of crane-related accident reports. Second, evaluation metrics and an expert questionnaire survey were developed to assess ChatGPT’s performance in CF extraction. Finally, CN analysis was conducted to explore the relationships among CFs and to identify critical causal paths. A total of 95 crane-related accidents from Hong Kong (2011-2020) were analyzed using the proposed framework. The critical CFs identified included: “carelessness”, “operation error”, “crane unbalanced”, “machine failure”, “parts of a crane fall”, “object strike”, “worker fall”, “trapping”, “collapse of crane”, and “load drop”. The critical path identified was: “broken/failed rope” → “load drop” → “object strike”. The primary contribution of this study lies in developing an AI-driven framework that combines the contextual understanding of ChatGPT with the structural analysis capabilities of CN methods—offering a novel and scalable approach to accident causation analysis in the construction industry. Safety managers and practitioners can leverage this framework to improve the automation, consistency, and interpretability of construction accident reporting.
Less.Yifan Wang, ... Jingjing Guo
DOI:https://doi.org/10.70401/jbde.2025.0009 - May 22, 2025
Insights and Issues of Implementing Virtual Reality (VR) for Supervision Training Purposes in SUBEB, Edo State, Nigeria
This study explores the adoption of Virtual Reality (VR) in the Nigerian construction industry, with a focus on its potential benefits and associated challenges. Purposive and snowball sampling techniques were employed to select 52 construction professionals ...
More.This study explores the adoption of Virtual Reality (VR) in the Nigerian construction industry, with a focus on its potential benefits and associated challenges. Purposive and snowball sampling techniques were employed to select 52 construction professionals from Benin, Edo State,an emerging urban center with extensive construction activity. Adopting a quantitative approach, the research utilized a five-point Likert scale survey to assess perceptions of the benefits and barriers to VR adoption. The survey was pretested for clarity and reliability, and data were collected via the Qualtrics platform. The findings indicate that the key benefits of VR include improved task-technology alignment, enhanced workplace safety through virtual training, and more effective remote collaboration. VR was also found to enrich user experience and learning engagement by simulating high-risk scenarios to aid hazard prevention. Nevertheless, the study identifies several critical barriers to adoption, such as uncertainty regarding learning outcomes, technical disruptions, and high implementation costs. Despite these limitations, VR holds considerable promise for transforming training and professional development in the construction sector. To maximize its impact, the study recommends the development of customized training modules, technological improvements to enhance system reliability, and government support to mitigate implementation costs. Overall, VR has the potential to significantly improve training effectiveness, safety standards, and operational efficiency in the Nigerian construction industry, provided that the identified barriers are adequately addressed.
Less.Osamwonyi Ada-okungbowa, ... Colin A. Booth
DOI:https://doi.org/10.70401/jbde.2025.0008 - May 17, 2025
Deep learning insights on the banning of engineered stone: decoding public sentiments in Australia
Amid growing global attention to occupational health and safety, the construction industry faces critical challenges associated with engineered stone, which emits high concentrations of respirable crystalline silica during processing and has been linked ...
More.Amid growing global attention to occupational health and safety, the construction industry faces critical challenges associated with engineered stone, which emits high concentrations of respirable crystalline silica during processing and has been linked to severe lung diseases. In response, Australia enacted a comprehensive nationwide ban on engineered stone in July 2024. Drawing on media framing theory, this study analyzes public discourse and sentiment surrounding the ban by examining 7,198 comments collected from Reddit and YouTube. Through Latent Dirichlet Allocation, three dominant themes emerged: health risks and safety concerns, economic impacts and industry transition, and regulatory implementation. Sentiment analysis revealed that 55.5% of the comments expressed negative sentiment, mainly centered on economic concerns, while 21.3% were positive, emphasizing health benefits, and 23.1% were neutral. Economic impact frames predominated among negative comments, whereas health risk frames were more common in positive ones. These findings suggest that future policy communications should more effectively integrate narratives around both health protection and economic transition. This study contributes to the methodological development of sentiment analysis and offers practical insights for policy formulation and implementation.
Less.Yuan Sheng, ... Jian Zuo
DOI:https://doi.org/10.70401/jbde.2025.0007 - May 15, 2025