-
Geromedicine (GER, Online ISSN 3106-8618) is a quarterly, gold open-access journal published by Science Exploration Press, offering a comprehensive platform for research in geroscience. Progress in geroscience - the study of aging - has laid the foundation for geromedicine, which focuses on evidence-based medical interventions to keep individuals and populations healthy and fit. Precision geromedicine will rely on aging biomarkers to assess an individual's biological aging process (gerodiagnosis) and apply targeted interventions to enhance health and longevity (gerotherapeutics). The new journal Geromedicine will lead the development of this emerging medical discipline. more >
Articles
Major depressive disorder as a driver of premature aging
-
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a risk factor for many aging-related medical conditions as well as cognitive decline and mortality. These and other types of observations indicate a premature aging phenotype associated with the conditions mentioned above. ...
MoreMajor depressive disorder (MDD) is a risk factor for many aging-related medical conditions as well as cognitive decline and mortality. These and other types of observations indicate a premature aging phenotype associated with the conditions mentioned above. Recent studies have started to elucidate the mechanisms underlying the link between MDD and premature aging, pointing towards novel treatments of this phenotype. In this review, we first present evidence linking MDD to a premature aging phenotype and its association with abnormalities in multiple hallmarks of biological aging. Next, we discuss implications for treatment in MDD, including the potential geroprotective effects of antidepressant treatment as well as the conceptualization of biological aging processes as targets for novel gerotherapeutic interventions. Finally, we highlight the importance of integrating mental health assessment into both research and clinical settings to fulfill the promises of the new medical discipline of Geromedicine in preventing age-related decline and extending healthspan in the aging population.
Less -
Breno S. Diniz, ... Eric J. Lenze
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2026.0015 - February 12, 2026
Implementation of artificial intelligence in the clinical management of longevity
-
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a central driver in healthy longevity medicine (HLM), offering new tools to characterize biological aging trajectories, identify preclinical physiological decline, and optimize interventions aimed at preserving ...
MoreArtificial intelligence (AI) has become a central driver in healthy longevity medicine (HLM), offering new tools to characterize biological aging trajectories, identify preclinical physiological decline, and optimize interventions aimed at preserving function throughout the lifespan by targeting age-related processes. HLM is increasingly recognized as a specialty focusing on the multidimensional process of aging, encompassing molecular, physiological, cognitive, and behavioral components, all of which generate complex, high-dimensional datasets that exceed the analytical capacity of traditional clinical approaches. AI methodologies, including machine learning and deep learning models capable of integrating large, multimodal data streams, provide the computational infrastructure required to produce actionable insights. In the clinical practice of HLM, AI further facilitates integration of converging domains, including continuous digital phenotyping enabled by wearables and sensors, advanced biomarker modeling, predictive modeling capable of forecasting risk trajectories and personalized intervention optimization through life models and digital twins. These models support anticipatory clinical management, shifting care from reactive disease treatment toward continuous preservation of physiological resilience. Despite rapid progress, the integration of AI into routine healthy longevity care requires careful consideration of data quality, algorithmic transparency, regulatory frameworks, population diversity, and clinical interpretability. Nonetheless, AI-driven healthy longevity management is beginning to allow biological aging to be quantified, targeted, and longitudinally monitored in clinical practice.
Less -
Evelyne Bischof, ... Dominika Wilczok
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2026.0014 - January 29, 2026
Brown adipose tissue decline in aging, a role for autophagy?
-
The decline in brown adipose tissue (BAT) activity is a hallmark of aging and is believed to contribute significantly to the loss of cold tolerance and the increased propensity for obesity with age. Paradoxically, unlike in many other tissues and organs, available ...
MoreThe decline in brown adipose tissue (BAT) activity is a hallmark of aging and is believed to contribute significantly to the loss of cold tolerance and the increased propensity for obesity with age. Paradoxically, unlike in many other tissues and organs, available evidence suggests that macroautophagy increases in BAT with aging. This aligns with observations of a negative correlation between thermogenic activity and macroautophagy in response to environmental factors such as ambient temperature, with evidence showing that macroautophagy is suppressed in thermogenically active BAT under cold conditions, and conversely, increased in warmer environments. Moreover, the activation of macroautophagy, particularly mitophagy, has been shown to be essential for the “whitening” process, whereby brown or beige adipose tissue loses its thermogenic phenotype and adopts characteristics of energy-storing white adipose tissue. In contrast, recent findings suggest that chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) is directly associated with BAT thermogenesis. In male mice, CMA tends to decline with age in BAT, and pharmacological activation of CMA can restore thermogenic activity. This may be due to a specific role of CMA in degrading thermogenesis-inhibiting factors that accumulate in aging BAT because of diminished CMA activity. Given the critical role of BAT in metabolic health, especially during aging, autophagic processes, and their potential druggability, emerge as a promising strategy to preserve thermogenic capacity and improve metabolic health in the elderly.
Less -
Joan Villarroya, ... Francesc Villarroya
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2026.0013 - January 20, 2026
Autophagy and mitophagy in age-related macular degeneration: Custodians of retinal longevity
-
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), primarily driven by dysfunction of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in the elderly. As the central hub for photoreceptor support, nutrient transport, and waste ...
MoreAge-related macular degeneration (AMD), primarily driven by dysfunction of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in the elderly. As the central hub for photoreceptor support, nutrient transport, and waste clearance, the RPE is particularly vulnerable to age-related stressors that disrupt proteostasis and mitochondrial quality control. Autophagy and mitophagy are essential regulators of RPE and retinal longevity, ensuring the turnover of damaged proteins and organelles while maintaining energy homeostasis. In AMD, these pathways become compromised, contributing to lipofuscin accumulation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and progressive cell death. This review examines the physiological roles of autophagy and mitophagy in retinal homeostasis, their dysregulation in AMD, and emerging therapeutic approaches aimed at restoring these protective processes. Targeting autophagy and mitophagy is a promising strategy to preserve vision and delay the progression of AMD.
Less -
Ignacio Javier Noorbergen, ... Patricia Boya
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2026.0012 - January 19, 2026
The regulation of cutaneous immunity and pathology by cellular senescence
-
Skin diseases affect nearly one quarter of the global population, with prevalence rising sharply among older adults. By 2050, the number of individuals over 60 years will double, making age-related dermatological conditions an increasing public health concern. ...
MoreSkin diseases affect nearly one quarter of the global population, with prevalence rising sharply among older adults. By 2050, the number of individuals over 60 years will double, making age-related dermatological conditions an increasing public health concern. A central process underlying aging is cellular senescence, a stable form of growth arrest induced by diverse stressors, including DNA damage, telomere attrition, and oncogenic signaling. Senescent keratinocytes, fibroblasts, melanocytes, and immune cells accumulate in the skin with age and secrete a pro-inflammatory senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) that actively shapes the cutaneous immune landscape. Although senescence can promote tissue repair and tumour suppression, the persistence of senescent cells drives inflammation, impairs immunity function, and contributes to pathology, a concept now termed senopathy. In this review, we first examine the crosstalk between senescent stromal and immune cells in human skin. Then we discuss how SASP from senescent fibroblasts inhibits the function of resident T cell, while senescent T cells adopt a paradoxical state, hyperfunctional yet non-proliferative, that can accelerate tissue damage. We further highlight the immune evasion strategies which enable senescent cells to persist and drive inflammaging. Insights from patients with Familial Melanoma Syndrome (germline CDKN2A mutations) illustrate how defective senescence pathways across multiple cell types impair cutaneous immunosurveillance and increase melanoma risk. Finally, we explore evidence for stromal- and immune-mediated cutaneous senopathies, including psoriasis, lupus, vitiligo, and leishmaniasis, where senescent cells actively drive the diseases’ progression. Based on the analysis, we propose that the skin represents a powerful and accessible model for investigating the interplay between senescent immune and non-immune cells across the lifespan, with therapeutic implications for aging and age-related pathologies.
Less -
Priya Subramanian, ... Arne N. Akbar
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0011 - December 18, 2025
Hallmarks of aging: Integrating molecular and social determinants
-
The biology of aging is increasingly understood through geroscience frameworks integrating molecular, cellular, physiological, and social hallmarks. Recently, we introduced psychosocial factors including mental illness as an important hallmark of ...
MoreThe biology of aging is increasingly understood through geroscience frameworks integrating molecular, cellular, physiological, and social hallmarks. Recently, we introduced psychosocial factors including mental illness as an important hallmark of aging. Indeed, exposome-centered approaches reveal complex interactions among socioeconomic, environmental, behavioral, and genomic factors. Precision Geromedicine aims to target all these determinants in a holistic fashion to improve aging trajectories and extend healthspan.
Less -
Carlos López-Otín, Guido Kroemer
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0007 - October 31, 2025
Clinical evidence for the use of NAD+ precursors to slow aging
-
Significant progress in clinical care has extended human life expectancy to unprecedented levels. However, this trend has been parallelled by a rise in years lived with poor health, posing profound challenges not only to individual quality of life, but also ...
MoreSignificant progress in clinical care has extended human life expectancy to unprecedented levels. However, this trend has been parallelled by a rise in years lived with poor health, posing profound challenges not only to individual quality of life, but also to substantial medical and socioeconomic burdens at the population level. This underscores the urgent need for strategies that extend healthspan alongside lifespan. In this regard, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) has emerged as a central metabolic cofactor and signaling molecule that regulates processes fundamental to health and longevity, including energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, inflammation, and DNA repair. Importantly, intracellular NAD+ levels decline with age across multiple tissues and organ systems, and restoring NAD+ content has been shown to reinstate cellular and physiological function in various model systems. Among the strategies to augment NAD+, supplementation with its precursors, namely nicotinic acid/niacin, nicotinamide, nicotinamide riboside, and nicotinamide mononucleotide, represents the most practical and extensively studied approach. Over the past two decades, preclinical research and an increasing number of clinical trials have investigated the therapeutic potential of these precursors in preventing or reversing age-associated decline and pathologies. In this review, we synthesize recent clinical advances, critically evaluate the promise and limitations of NAD+ precursor supplementation, and discuss future directions for leveraging NAD+ metabolism to improve healthspan in a rapidly aging global population.
Less -
Subhash Khatri, ... Simon Sedej
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0008 - November 17, 2025
The vocabulary of geromedicine: gerovocabulary
-
Guido Kroemer, ... Andrea B. Maier
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0002 - May 07, 2025
Geromedicine: A new journal for the clinical application of geroscience
-
Guido Kroemer, ... Andrea B. Maier
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0001 - May 07, 2025
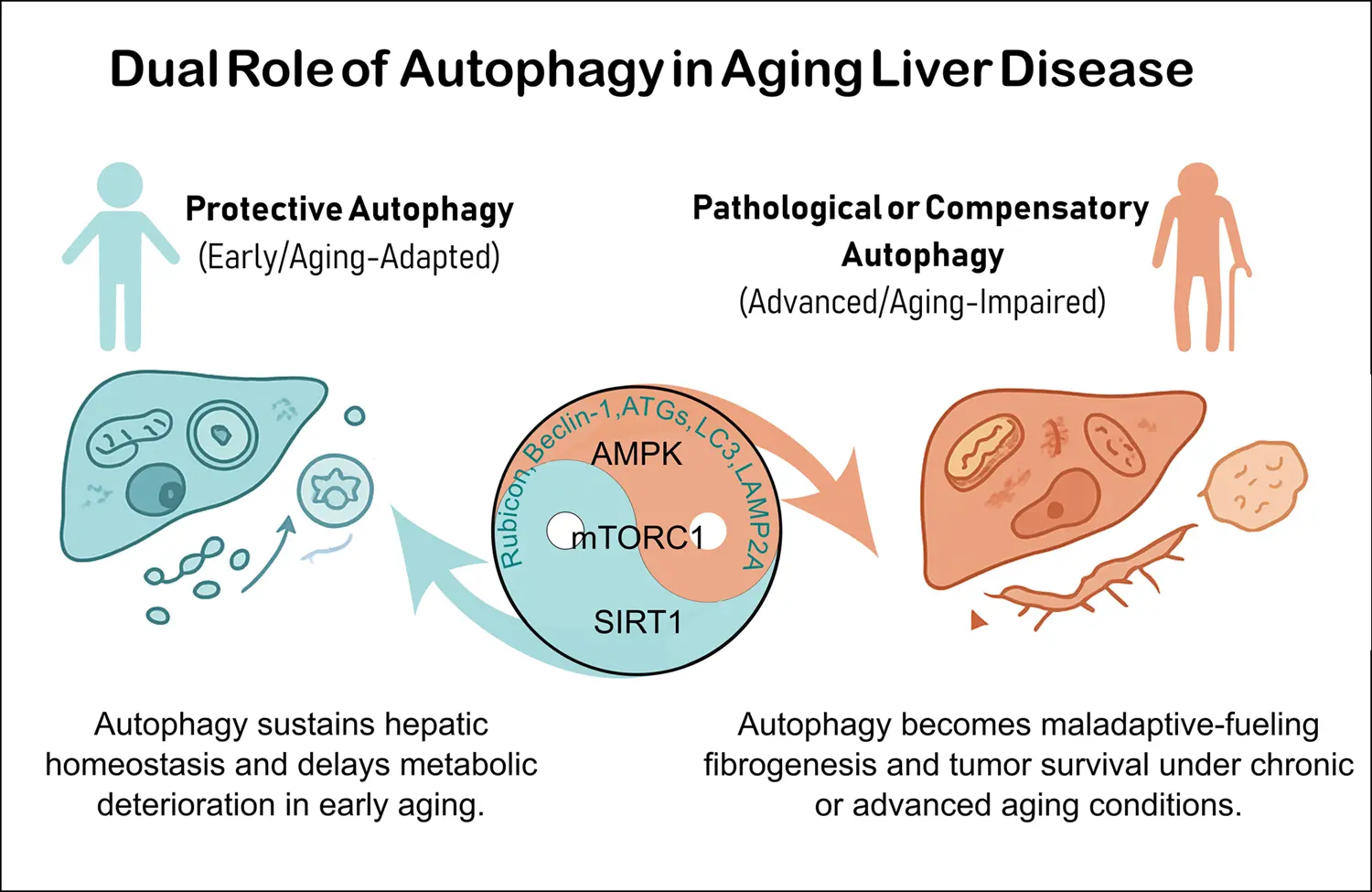
Autophagy in age-related liver disease
-
Aging profoundly impacts liver physiology by disrupting autophagy, a lysosome-dependent degradation pathway essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis. Autophagy declines with aging due to reduced expression of core autophagy-related (ATG) genes/proteins, ...
MoreAging profoundly impacts liver physiology by disrupting autophagy, a lysosome-dependent degradation pathway essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis. Autophagy declines with aging due to reduced expression of core autophagy-related (ATG) genes/proteins, defective autophagosome fusion, and impaired selective processes such as lipophagy, mitophagy, and chaperone-mediated autophagy. These alterations contribute to lipid accumulation, oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction, thereby accelerating age-related liver diseases including metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), fibrosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Their molecular mechanisms involve deregulation of nutrient-sensing pathways (mTOR complex 1, AMP-activated protein kinase and sirtuin 1 and 3) and context-dependent roles of autophagy-related proteins (ATG5, ATG7, LC3, Beclin-1, LAMP2A). Importantly, the regulatory role of autophagy differs across disease stages related to liver aging. During early phases, it maintains metabolic balance, mitochondrial quality control, and genomic stability in some diseases such as MAFLD and liver fibrosis. Conversely, in advanced disease, particularly in HCC, persistent autophagy supports tumor cell survival, stemness, and immune evasion. Emerging therapies seek to restore autophagic flux through caloric restriction, physical exercise, caloric restriction mimetics (rapalogs, spermidine, metformin), and pharmacological modulators such as Tat-BECLIN-1 peptides or RUBICON-targeted approaches. However, translating these therapies into clinical practice remains challenging due to systemic effects, stage-specific responses, and lack of reliable non-invasive biomarkers for monitoring autophagy in humans. Advances in nanoparticle-based delivery, biomarker-guided stratification, and combination therapies with tyrosine kinase inhibitors or immune checkpoint inhibitors may offer promising strategies. Overall, precision modulation of autophagy could serve as a potent geroprotective approach to preserve liver function, delay age-related metabolic deterioration, and prevent progression to fibrosis and cancer. Achieving this goal requires considering disease stage, systemic interactions, and autophagy’s context-dependent duality in aging when implementing these strategies.
Less -
Roberto Palacios-Ramírez, ... Omar Motiño García-Miguel
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0005 - October 17, 2025
Hallmarks of aging: Integrating molecular and social determinants
-
The biology of aging is increasingly understood through geroscience frameworks integrating molecular, cellular, physiological, and social hallmarks. Recently, we introduced psychosocial factors including mental illness as an important hallmark of ...
MoreThe biology of aging is increasingly understood through geroscience frameworks integrating molecular, cellular, physiological, and social hallmarks. Recently, we introduced psychosocial factors including mental illness as an important hallmark of aging. Indeed, exposome-centered approaches reveal complex interactions among socioeconomic, environmental, behavioral, and genomic factors. Precision Geromedicine aims to target all these determinants in a holistic fashion to improve aging trajectories and extend healthspan.
Less -
Carlos López-Otín, Guido Kroemer
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0007 - October 31, 2025
Clinical evidence for the use of NAD+ precursors to slow aging
-
Significant progress in clinical care has extended human life expectancy to unprecedented levels. However, this trend has been parallelled by a rise in years lived with poor health, posing profound challenges not only to individual quality of life, but also ...
MoreSignificant progress in clinical care has extended human life expectancy to unprecedented levels. However, this trend has been parallelled by a rise in years lived with poor health, posing profound challenges not only to individual quality of life, but also to substantial medical and socioeconomic burdens at the population level. This underscores the urgent need for strategies that extend healthspan alongside lifespan. In this regard, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) has emerged as a central metabolic cofactor and signaling molecule that regulates processes fundamental to health and longevity, including energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, inflammation, and DNA repair. Importantly, intracellular NAD+ levels decline with age across multiple tissues and organ systems, and restoring NAD+ content has been shown to reinstate cellular and physiological function in various model systems. Among the strategies to augment NAD+, supplementation with its precursors, namely nicotinic acid/niacin, nicotinamide, nicotinamide riboside, and nicotinamide mononucleotide, represents the most practical and extensively studied approach. Over the past two decades, preclinical research and an increasing number of clinical trials have investigated the therapeutic potential of these precursors in preventing or reversing age-associated decline and pathologies. In this review, we synthesize recent clinical advances, critically evaluate the promise and limitations of NAD+ precursor supplementation, and discuss future directions for leveraging NAD+ metabolism to improve healthspan in a rapidly aging global population.
Less -
Subhash Khatri, ... Simon Sedej
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0008 - November 17, 2025
The vocabulary of geromedicine: gerovocabulary
-
Guido Kroemer, ... Andrea B. Maier
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0002 - May 07, 2025
Tau protein isoforms in neuropathological aging: Gerosuppressors, gerogenes or just travel companions
-
In recent years, the terms “gerosuppressors” and “gerogenes” have been introduced to describe factors that respectively delay or accelerate aging. These factors are present across various cell types. Specific proteins, such as tau predominantly expressed ...
MoreIn recent years, the terms “gerosuppressors” and “gerogenes” have been introduced to describe factors that respectively delay or accelerate aging. These factors are present across various cell types. Specific proteins, such as tau predominantly expressed in neurons, may act as neuron-specific gerosuppressors or gerogenes. Tau exhibits a dual role influenced by its post-translational modifications, particularly phosphorylation. In this review, we discuss relevant examples of tau isoforms that demonstrate both roles, underscoring its dual influence on neuronal aging.
Less -
Jesús Avila, ... José Viña
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2025.0006 - October 17, 2025
Implementation of artificial intelligence in the clinical management of longevity
-
Artificial intelligence (AI) has become a central driver in healthy longevity medicine (HLM), offering new tools to characterize biological aging trajectories, identify preclinical physiological decline, and optimize interventions aimed at preserving ...
MoreArtificial intelligence (AI) has become a central driver in healthy longevity medicine (HLM), offering new tools to characterize biological aging trajectories, identify preclinical physiological decline, and optimize interventions aimed at preserving function throughout the lifespan by targeting age-related processes. HLM is increasingly recognized as a specialty focusing on the multidimensional process of aging, encompassing molecular, physiological, cognitive, and behavioral components, all of which generate complex, high-dimensional datasets that exceed the analytical capacity of traditional clinical approaches. AI methodologies, including machine learning and deep learning models capable of integrating large, multimodal data streams, provide the computational infrastructure required to produce actionable insights. In the clinical practice of HLM, AI further facilitates integration of converging domains, including continuous digital phenotyping enabled by wearables and sensors, advanced biomarker modeling, predictive modeling capable of forecasting risk trajectories and personalized intervention optimization through life models and digital twins. These models support anticipatory clinical management, shifting care from reactive disease treatment toward continuous preservation of physiological resilience. Despite rapid progress, the integration of AI into routine healthy longevity care requires careful consideration of data quality, algorithmic transparency, regulatory frameworks, population diversity, and clinical interpretability. Nonetheless, AI-driven healthy longevity management is beginning to allow biological aging to be quantified, targeted, and longitudinally monitored in clinical practice.
Less -
Evelyne Bischof, ... Dominika Wilczok
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/Geromedicine.2026.0014 - January 29, 2026
Special Issues
Understudied Directions in Aging Biology, Quantitative and First-Principles Approaches
-
Submission Deadline: 14 Feb 2026
-
Published articles: 0