All Articles
Ru-TiO2 nanosphere arrays: Efficient nitrate reduction catalyst under strongly acidic and high-salinity conditions
-
Yicheng Li, ... Zhurui Shen
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0022 - December 26, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Liquid manipulating interfaces from natural prototypes to emerged devices
-
The aggregation, distribution, spreading, elongation and shrinking, as well as other behaviors of liquids, along with mass transfer and thermal exchange, are ubiquitous in both natural creatures and human daily life. These phenomena greatly inspire the ...
MoreThe aggregation, distribution, spreading, elongation and shrinking, as well as other behaviors of liquids, along with mass transfer and thermal exchange, are ubiquitous in both natural creatures and human daily life. These phenomena greatly inspire the advancement of liquid manipulating interfaces in theoretical models, production processes, and performance optimization. After decades of development, regulating liquid movements through surface chemistry, micro/nano structures, and geometrical gradients is becoming increasingly prevalent but still faces challenges. This review discusses the design principles of liquid manipulating interfaces, bionic prototypes and its models behind, and introduces their specific role within these works. We summarize state-of-the-art works from different motion dimensions, as well as the most widely mentioned applications. We believe this can inspire the transfer of bioinspired structures into functional devices through continued innovative breakthroughs and multidisciplinary collaboration.
Less -
Jiasong Liu, ... Moyuan Cao
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0021 - December 18, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Immobilized photocatalyst devices for scalable overall water splitting
-
Immobilized photocatalyst devices for overall water splitting (OWS) have emerged as a promising strategy for practical hydrogen production. Compared with traditional powder suspension systems, they offer great advantages, including scalability, facile ...
MoreImmobilized photocatalyst devices for overall water splitting (OWS) have emerged as a promising strategy for practical hydrogen production. Compared with traditional powder suspension systems, they offer great advantages, including scalability, facile recovery/replacement of photocatalysts, and the elimination of extra dispersion operations. Over the past decade, significant progress has been achieved in this field, especially in material screening, device construction, and system integration for scalable applications. However, up until now, there have been no related reviews focusing on this topic. This review aims to fill this gap by providing a comprehensive and structured overview of the immobilized photocatalyst devices for efficient OWS. Firstly, the basics of OWS process, including one-step and two-step photoexcitation mechanisms, are elaborated. Subsequently, recent advances in immobilized photocatalyst devices for scalable OWS via these two different approaches are summarized, based on which various solid-state electron mediators are classified and exemplified. The essential structure-performance relationship is also analyzed and revealed. Finally, the future prospects and challenges in this field are proposed and discussed.
Less -
Yifan Shao, ... Shanshan Chen
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0020 - December 17, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Preface of Special Issue on Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
-
Zhong-Yong Yuan
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0019 - November 11, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Investigation of wheel-rail wear reduction by using MRF rubber joints with bidirectional adjustable stiffness
-
Stiffness of the primary longitudinal rubber joints is critical for both the high-speed stability and curve trafficability of the train. However, existing joints with fixed stiffness inevitably generate large wheel-rail lateral forces and wear on curves. ...
MoreStiffness of the primary longitudinal rubber joints is critical for both the high-speed stability and curve trafficability of the train. However, existing joints with fixed stiffness inevitably generate large wheel-rail lateral forces and wear on curves. To address this issue, a fail-safe rubber joint incorporating magnetorheological fluid (MRF) technology is proposed, enabling bidirectional variable stiffness. First, the structure and working principle of MRF rubber joint are described in detail. Subsequently, prototypes of the MRF damper and the MRF rubber joint are assembled and tested, yielding satisfactory variable damping and stiffness performance. Moreover, dynamic simulations further demonstrate the joint’s effectiveness in improving both stability and curve trafficability. A control algorithm based on track curvature identification is also proposed. The co-simulation results validate the potential of the MRF rubber joint on reducing wheel-rail wear and enhancing safety of trains.
Less -
Ning Gong, ... Shuaishuai Sun
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0018 - September 30, 2025
Electrocatalytic alcohol and aldehyde oxidation: advances in catalysts and reaction mechanisms for sustainable chemical synthesis
-
Electrocatalytic oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes, known as alcohol oxidation reactions (AOR), provides a sustainable and efficient route for converting low-value feedstocks such as ethanol, glycerol, and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into high-value ...
MoreElectrocatalytic oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes, known as alcohol oxidation reactions (AOR), provides a sustainable and efficient route for converting low-value feedstocks such as ethanol, glycerol, and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into high-value chemicals, including organic acids and aldehydes, in line with the chemical industry’s transition toward carbon neutrality. This review synthesizes recent advancements in electrocatalytic AOR, emphasizing advances in catalyst design and detailed reaction mechanisms. A broad spectrum of catalysts is explored, ranging from noble metal-based (e.g., Pt, Pd, Au) to cost-effective non-noble metal-based (e.g., Ni, Cu, Co) materials, with attention to advanced strategies such as heteroatom doping, vacancy engineering, and alloying for fine-tuning electronic structures and optimizing intermediate adsorption. The review also delves into mechanistic insights, elucidating rate-determining steps, adsorption geometries, and electron-transfer pathways that govern AOR performance, supported by density functional theory analyses. Special emphasis is placed on the interplay between catalyst electronic structure and reaction kinetics, offering fresh perspectives for improving yield, selectivity, and Faradaic efficiency. Finally, current challenges, including catalyst stability, product selectivity, and scalability, are critically evaluated, and future directions such as in situ characterization and the development of non-noble metal catalysts are proposed to advance AOR toward large-scale, sustainable chemical synthesis.
Less -
Lei Chen, Zhong-Yong Yuan
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0017 - September 28, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
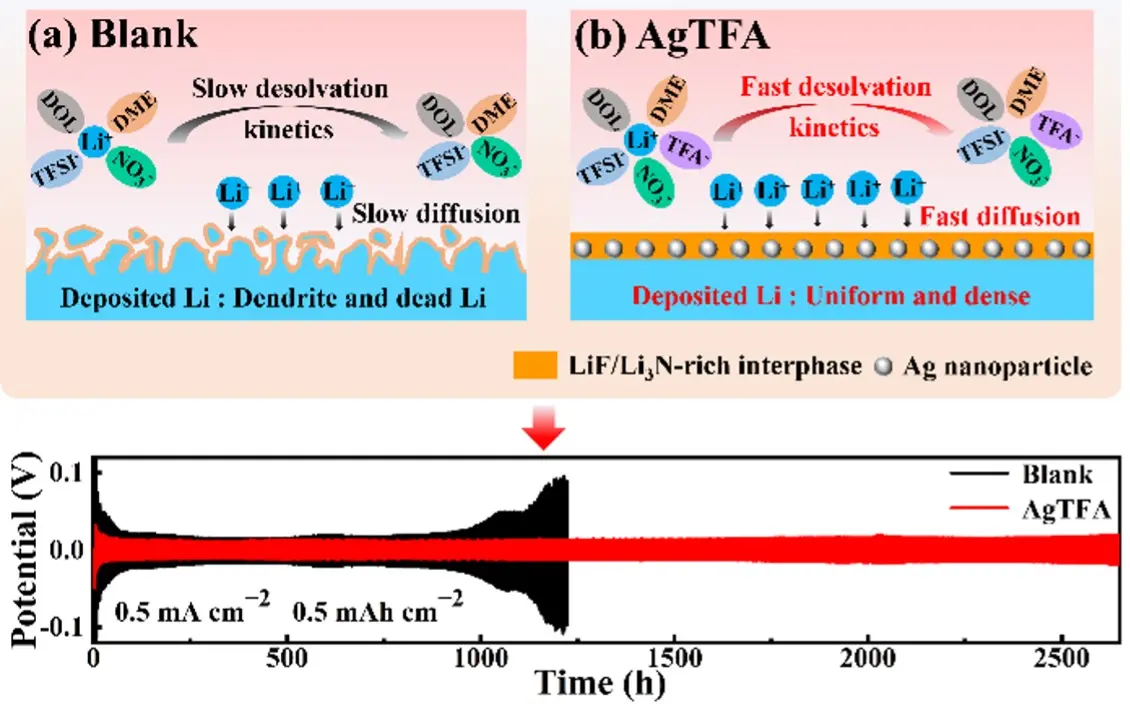
Synergistic regulation of lithium nucleation and anion-rich solvation structure via silver trifluoroacetate additive for stable lithium metal anodes
-
Lithium (Li) metal, owing to its high theoretical specific capacity and low electrochemical potential, is considered one of the most promising anode materials for next-generation rechargeable batteries. However, interfacial instability severely hinders ...
MoreLithium (Li) metal, owing to its high theoretical specific capacity and low electrochemical potential, is considered one of the most promising anode materials for next-generation rechargeable batteries. However, interfacial instability severely hinders the practical application of Li anodes. Constructing a robust solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) with optimized chemical composition and structure has been recognized as an effective strategy to overcome this challenge. Here, we propose silver trifluoroacetate (AgTFA) as a multifunctional electrolyte additive that synergistically regulates Li nucleation and promotes the formation of an anion-rich solvation structure. Through a spontaneous in situ displacement reaction, uniformly distributed silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) are generated on the Li surface, providing abundant lithiophilic nucleation sites to enable homogeneous Li deposition. Meanwhile, trifluoroacetate anions (TFA-) with an ultrahigh donor number, together with NO3- anions participating in Li+ solvation, markedly reduce the desolvation barrier and facilitate the formation of a LiF-Li3N-rich SEI. As a result, Li||Li symmetric cells exhibit remarkable cycling stability of up to 2,500 hours at 0.5 mA·cm-2/0.5 mAh·cm-2, while Li||LiFePO4 full cells deliver a high discharge capacity of 139.8 mAh·g-1 with an excellent capacity retention of 97.28% after 200 cycles at 1.0 C. This work demonstrates a feasible strategy for constructing durable SEI layers by coupling Li nucleation regulation with anion-rich solvation chemistry.
Less -
Jing Bai, ... Sheng Liu
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0016 - September 26, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Elevating electrode catalyst stabilization for long-term intermittent alkaline seawater electrolysis
-
Lei Wang, Zhong-Yong Yuan
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0015 - September 16, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
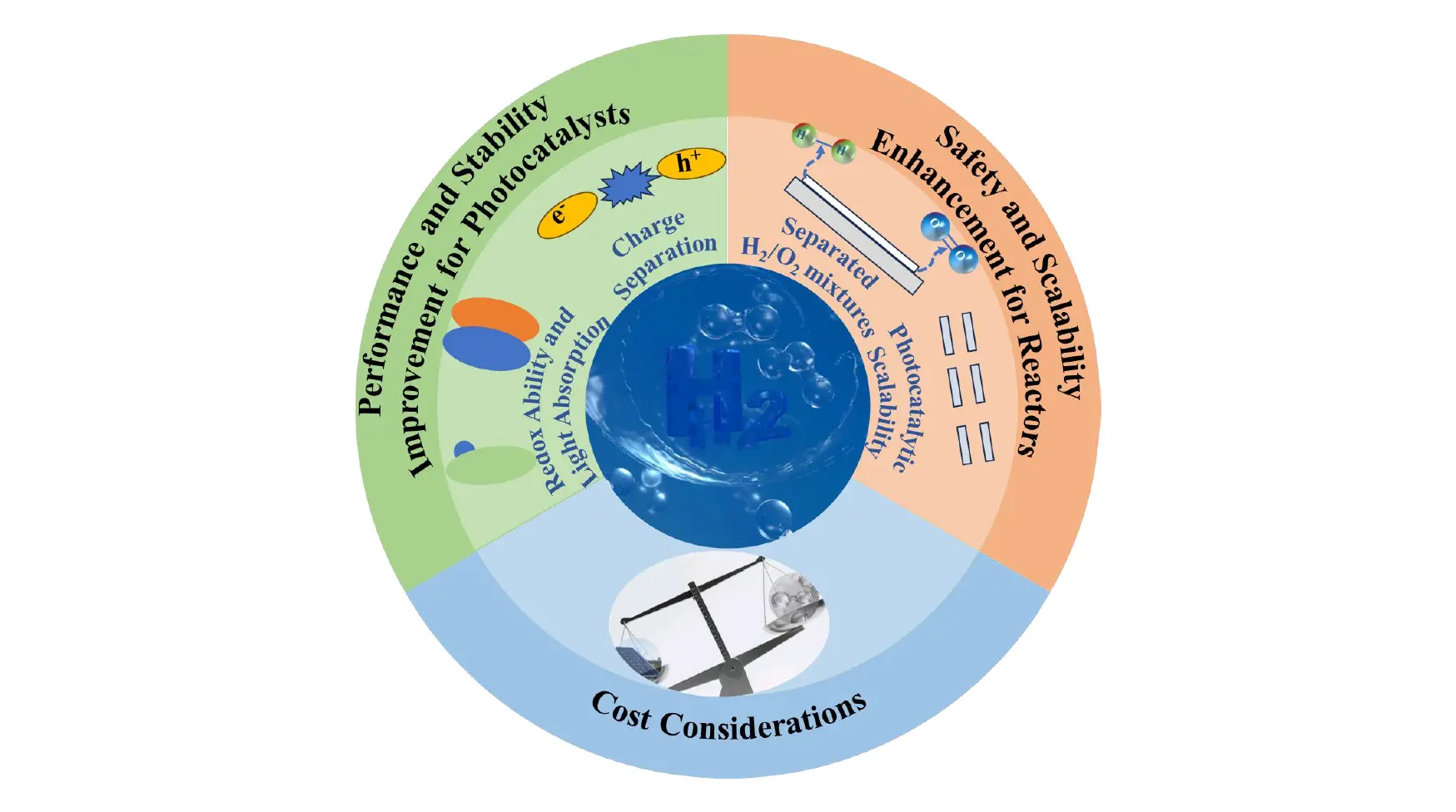
Key requirements for photocatalysts and reactor architectures toward large-scale hydrogen generation
-
Green hydrogen produced through photocatalytic water splitting is pivotal for achieving carbon neutrality and facilitating the transition to carbon-free energy conversion systems. Although photocatalytic systems have demonstrated high activity and ...
MoreGreen hydrogen produced through photocatalytic water splitting is pivotal for achieving carbon neutrality and facilitating the transition to carbon-free energy conversion systems. Although photocatalytic systems have demonstrated high activity and operational safety at the laboratory scale, their large-scale application for practical hydrogen production remains limited by the long-term stability and performance of photocatalysts, as well as the complexity and safety concerns associated with scaling up photocatalytic reaction platforms. Meeting these requirements would establish a targeted framework for advancing photolysis technology and accelerating the transition from fundamental research to industrial-scale implementation of photocatalytic hydrogen generation. This perspective highlights the fundamental principles for improving photocatalysis and explores diverse device configurations for large-scale hydrogen production, while outlining the critical prerequisites for both photocatalytic materials and reactor architectures, thereby paving the way for future commercialization.
Less -
Xiaoshuai Wang, Zhong-Yong Yuan
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0014 - September 12, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Engineering of transition metal phosphide-based heterostructures for electrocatalytic water splitting
-
Transition metal phosphides (TMPs) have been recognized as promising electrocatalysts for water splitting due to their high electronic conductivity, tunable structure and composition, and multifunctional active sites. Combining TMPs with other materials ...
MoreTransition metal phosphides (TMPs) have been recognized as promising electrocatalysts for water splitting due to their high electronic conductivity, tunable structure and composition, and multifunctional active sites. Combining TMPs with other materials such as metals and compounds to form heterostructures can significantly enhance electrocatalytic performance. This review summarizes recent advances in TMP-based heterostructures for electrocatalytic water splitting. The design of electrocatalyst structures and compositions, along with their corresponding electrochemical activities, is discussed. Emphasis is placed on interfacial engineering and the synergistic effects between heterocomponents to elucidate the relationship between interfacial characteristics and catalytic performance. Finally, current challenges and future research directions for TMP-based heterostructure electrocatalysts in water splitting are proposed.
Less -
Hui Zhao, Zhong-Yong Yuan
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0013 - July 18, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Triaxial tactile sensing for next-gen robotics and wearable devices
-
Triaxial tactile sensing technology overcomes the limitations of conventional single-axis sensors by enabling real-time decoupling of normal and shear forces, thereby supporting multi-dimensional perception in robotics, wearable devices, and human-computer ...
MoreTriaxial tactile sensing technology overcomes the limitations of conventional single-axis sensors by enabling real-time decoupling of normal and shear forces, thereby supporting multi-dimensional perception in robotics, wearable devices, and human-computer interaction. By integrating flexible electronics with high-density sensor arrays, this technology enables precise object manipulation, environmental mapping, and physiological monitoring. Current applications include haptic feedback in virtual reality/augmented reality, electronic skin, and robotic slip control, demonstrating high sensitivity, fast response, and high spatial resolution. The core challenge lies in simultaneously optimizing sensing performance, long-term durability, and integration feasibility. Advances in nanomaterial engineering and machine learning algorithms are improving the accuracy of force decoupling and the efficiency of signal processing. This review systematically examines the working principles, strategies for performance enhancement, data processing methods, and cross-domain applications of triaxial tactile sensing. Instead of focusing primarily on materials or individual sensing mechanisms, it highlights critical performance trade-offs and co-optimization frameworks involving sensing performance, durability, and integration, to promote the widespread adoption of intelligent tactile systems across various industries.
Less -
Guolin Yun, Zhiwei Hu
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0012 - June 29, 2025
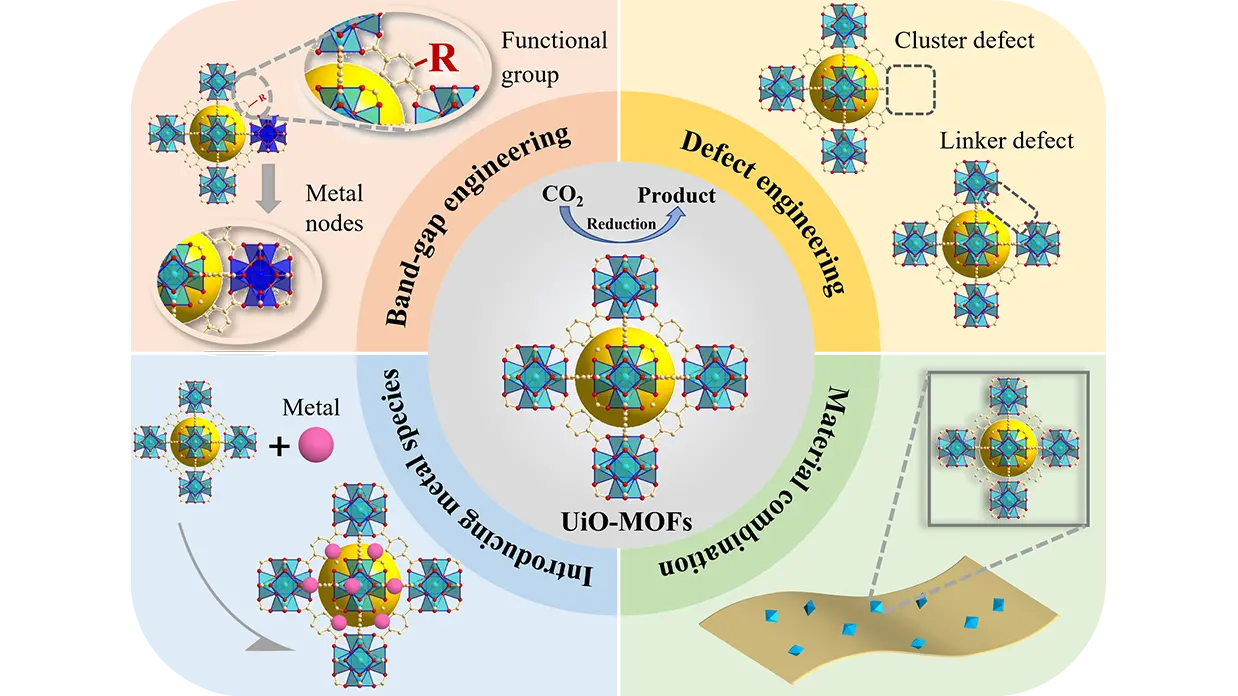
UiO series of MOFs and their composites for photocatalytic CO2 reduction: A review
-
Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to produce valuable fuels or chemicals is a promising CO2 utilization technology, which is of great significance for carbon emission reduction. The unique features of the UiO series of metal-organic ...
MorePhotocatalytic reduction of CO2 to produce valuable fuels or chemicals is a promising CO2 utilization technology, which is of great significance for carbon emission reduction. The unique features of the UiO series of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), such as the excellent water and chemical stability, notable structural tunability, broad and adjustable light-harvesting capacity, strong electron-hole separation ability, and high porosity and specific surface area, make them a class of photocatalysts with great potential for the CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR). Significant progress has been made in the development of efficient UiO-based photocatalysts for CO2RR. This paper provides a summary of recent research advances in UiO-MOFs for photocatalytic CO2RR. The characteristics, synthesis methods, and modifications of UiO-based materials, along with their photocatalytic performance, are described. Various modification strategies for UiO-MOFs, including band-gap engineering, defect engineering, introduction of metal species, and construction of composite materials, are summarized and discussed. The challenges facing UiO-MOFs in photocatalytic CO2RR and potential future development directions are also presented. This review is intended to provide insights into CO₂ photoreduction using UiO-based materials and to encourage further research and development in this promising field.
Less -
Liqing Shi, ... Lan-Lan Lou
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0011 - May 20, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Management of charge and exciton for high-performance and long-lifetime blue OLEDs
-
High-performance and long-lifetime blue organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) are crucial for meeting the demands of advanced display and lighting technologies. Despite high device efficiency has been achieved in blue OLEDs, development of high-performance ...
MoreHigh-performance and long-lifetime blue organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) are crucial for meeting the demands of advanced display and lighting technologies. Despite high device efficiency has been achieved in blue OLEDs, development of high-performance and long-lifetime blue OLEDs still lag far behind their red/green counterparts due to the presence of long-lived high-energy triplet excitons and polarons. Given the critical role of charge and exciton management in both the emission and degradation processes of OLEDs, this review systematically summarizes strategies for suppressing charge leakage and exciton quenching, as well as for enhancing exciton utilization in blue fluorescent, phosphorescent, and thermally activated delayed fluorescent (TADF) OLEDs. In this context, we further discuss the roles of conventional fluorescent hosts, triplet-triplet annihilation/hot exciton hosts, TADF assistant hosts, phosphorescent assistant hosts, and exciplex/electroplex hosts in regulating charge and exciton dynamics in blue OLEDs. Additionally, the modification of emitting layer materials is highlighted as a key strategy for managing charge and exciton processes in efficient and stable solution-processed blue OLEDs. Based on current insights into the efficiency and operational stability of blue OLEDs, this review proposes feasible charge and exciton management strategies to address the current challenges.
Less -
Zhizhi Li, ... Shi-Jian Su
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0009 - April 11, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards High-Performance and Long-Lifetime OLEDs
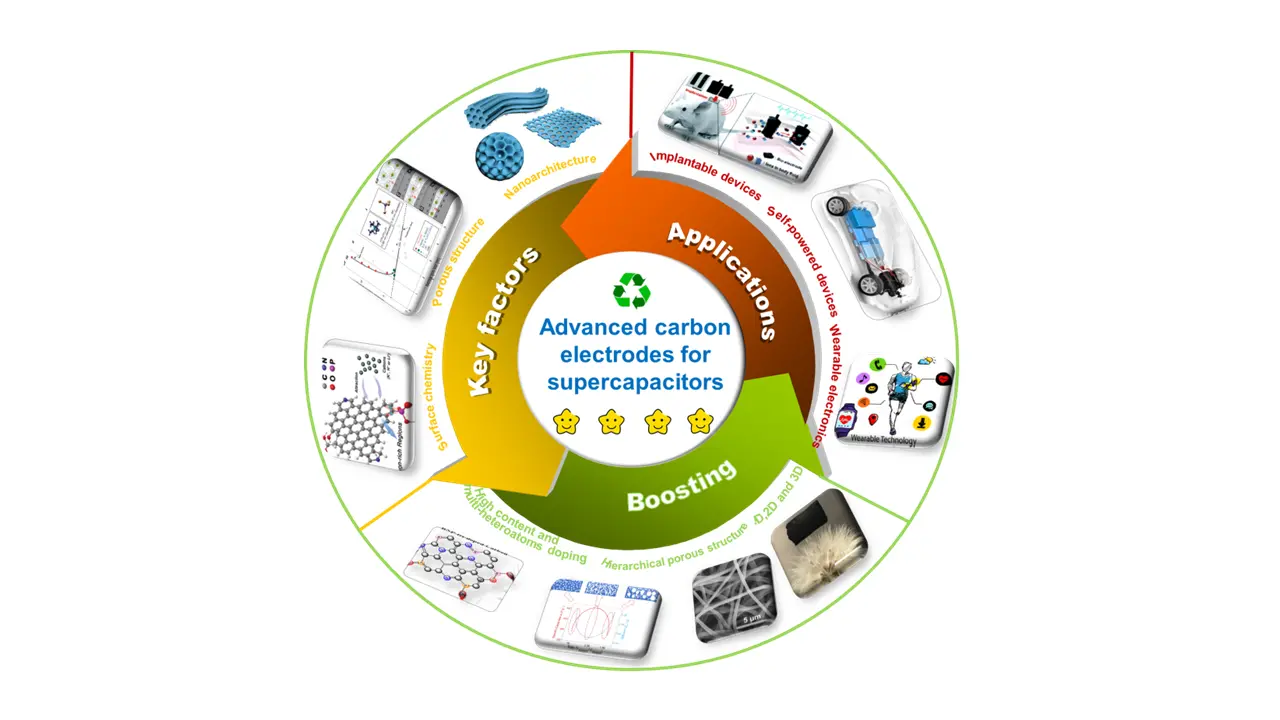
Advanced carbon electrodes for supercapacitors: design strategies, performance optimization, and practical applications
-
Supercapacitors, renowned for their high-power density, rapid charge/discharge capabilities, and exceptional cycling stability, have emerged as promising solutions for sustainable and efficient energy storage. Among various electrode materials, ...
MoreSupercapacitors, renowned for their high-power density, rapid charge/discharge capabilities, and exceptional cycling stability, have emerged as promising solutions for sustainable and efficient energy storage. Among various electrode materials, carbon materials stands out due to its abundance, excellent electrical conductivity, chemical stability and structural versatility. This review explores the design strategies, performance optimization, and the expanding applications of carbon-based electrodes for supercapacitors. We first analyze the key factors that impact the performance of carbon electrodes for supercapacitors, including pore structure, surface chemistry, electrical conductivity and nanoscale architecture. Subsequently, we provide an in-depth analysis of recent advancements in the rational design of carbon materials, focusing on strategies for optimizing pore architecture, functionalizing surfaces, enhancing conductivity and designing nanostructures. By addressing performance limitations, the review highlights strategies that have significantly improved the efficiency of carbon electrodes. Furthermore, we explore the practical applications of carbon-based supercapacitors in wearable electronics,
Lessself-powered devices, and implantable systems. Lastly, we discuss the challenges and opportunities associated by carbon-based electrodes from the perspective of electrode design and practical application. -
Lei Liu, ... Ruliang Zhang
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0008 - March 18, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Materials innovation for circularly polarized photodetectors
-
Circularly polarized light (CPL) features electromagnetic vectors that rotate regularly in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation, transmitting optical chirality information that is imperceptible to human beings. CPL can be classified ...
MoreCircularly polarized light (CPL) features electromagnetic vectors that rotate regularly in a plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation, transmitting optical chirality information that is imperceptible to human beings. CPL can be classified into the left-handed and right-handed circularly polarization light (L-/R-CPL), depending on whether the rotation direction is clockwise or anticlockwise, respectively. The ability to manipulate and characterize CPL is crucial for advancing various optical technologies, making the effective and direct detection of CPL extremely important. Breeding in the hotbed provided by the explosively increased chiral materials with CPL luminescence and strong circular dichroism (CD), CPL detectors are currently experiencing savage growth. Mainstream strategies can be divided into the leverage of photoactive materials with inherent chirality and the integration of chiral metamaterials with nonchiral photoactive materials. In this review, we not only highlight significant material innovations and detector architectures for CPL detection but also address the broader implications of these advancements. We discuss the challenges and future directions in this field, particularly focusing on how these developments could impact existing commodities, such as polarimetric imaging and security communications, and contribute to sustainability in technology through improved detection efficiency. Our goal is to inspire further promising developments in CPL photodetectors and encourage a broader application spectrum.
Less -
Jiajia Zha, ... Chaoliang Tan
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0006 - March 12, 2025
Introducing Smart Materials and Devices
-
Zhong-Yong Yuan, ... Weihua Li
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0007 - March 10, 2025
Mechanical properties of magnetorheological shear thickening fluid and its application in dampers
-
Magnetorheological fluid (MRF) has broad application prospects in the field of engineering vibration damping due to its magnet-sensitive characteristics. However, owing to its dependence on external electric or magnetic fields, devices based on MRF can’t ...
MoreMagnetorheological fluid (MRF) has broad application prospects in the field of engineering vibration damping due to its magnet-sensitive characteristics. However, owing to its dependence on external electric or magnetic fields, devices based on MRF can’t work once the power is turned off. Here we developed a magnetorheological shear thickening fluid (MRSTF) with both the magnet-sensitive and rate-sensitive characteristics. The shear thickening effect of MRSTF was examined, revealing that the critical shear rate
Lessof the suspension gradually decreases from 79.4 s-1 to 30.2 s-1 and the shear thickening power β of the suspension gradually decreases from 0.27 to 0.19 as the carbonyl iron powder (CIP) content increases from 0 to 30 vol.% when the mass fraction of SiO2 is 54 wt.%. Besides, the MRSTF-based dampers were tested under different frequencies and amplitudes. The results show that the MRSTF-based dampers still exhibit the energy dissipation characteristics in the absence of magnetic field because of the rate-sensitive property of MRSTF. Under the condition of an applied magnetic field, the dampers exhibit stronger energy dissipation characteristics due to the magnetic-sensitive characteristics of MRSTF. Concurrently, the dissipation capacity of the dampers increases with the increase of frequency and amplitude. This work provides an approach to enhance the mechanical properties of dampers and widen the application field. -
Quan Liu, ... Xinglong Gong
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0005 - March 03, 2025
In-situ mechanical exfoliation of graphite to UV curable graphene/acrylate coatings and their corrosion resistance properties
-
Incorporation of two dimensional (2D) materials into a polymer matrix is an efficient way to prepare high performance coatings. Here we report the in-situ mechanical exfoliation of graphite in a mixture of hydroxyethylacrylate terminated polybutadiene ...
MoreIncorporation of two dimensional (2D) materials into a polymer matrix is an efficient way to prepare high performance coatings. Here we report the in-situ mechanical exfoliation of graphite in a mixture of hydroxyethylacrylate terminated polybutadiene urethane (HTPU) prepolymer and reactive diluent. The mixture containing exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets (GN) is directly used to prepare UV cured composite resins (G/HTPU) with various GN concentrations. Various techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Raman, atomic force microscopy (AFM), have been used to characterize the GN, confirming that few-layered GN are obtained after the in-situ mechanical exfoliation. The incorporation of GN exerts little effect on the curing of the coatings with a gelation around 95%, but greatly enhances the elastic modulus. Tafel polarization curves, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and salt-spray testing were conducted to comparatively evaluate the G/HTPU coatings with different GN loadings. The results indicate that the incorporation of GN greatly improves the corrosion resistance of the HTPU UV coatings. The self-corrosion current density (Icorr) and the charge transfer resistance (Rc) of
LessG/HTPU-2 (0.2% GN loading) are greatly reduced to 1.03 × 10-8 A·cm-2 and increased by two magnitudes, respectively, compared to those of the parent HTPU coating. Additionally, the G/HTPU-2 coating with thickness of 100 μm can protect galvanized sheet against 0.5 mol/l sulfuric acid for at least 24 h. The practical application in protection of electronics was illustrated by coating the G/HTPU-2 on a standard printed circuit board (PCB, IPC-B-24A). No corrosion was observed after it was immersed in an artificial sweat solution even under open-circuit voltage of 12 V for 72 h and then 24 V for 48 h. -
Zihan Shen, ... Qiang Xiao
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0004 - February 17, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Smart Porous Materials and Catalysis
Highly efficient hybrid tandem white organic light-emitting diodes with two different color-emitting units
-
White-color organic light-emitting diodes (WOLEDs) have aroused wide interests for future lighting because of low energy consumption in principle, while still suffer from the degradation by Joule heating and polaron-induced quenching under high luminance ...
MoreWhite-color organic light-emitting diodes (WOLEDs) have aroused wide interests for future lighting because of low energy consumption in principle, while still suffer from the degradation by Joule heating and polaron-induced quenching under high luminance caused by high current in practical. To obtain high current efficiency, which means high luminance at low current density, tandem WOLEDs with multiple electroluminescence (EL) units connected in series with charge generation layers (CGLs) have been developed. Here we report the improved hybrid tandem WOLED with two EL units, EL1 and EL2, where EL1 and EL2 generate fluorescent blue and phosphorescent yellow emissions from a metal-free material BCzVBi and a Ir-complex (fbi)2Ir(acac), respectively, with CGL composed of a HATCN/NPB bilayer. The white-light emitting device shows the maximum current efficiency and power efficiency of 60.2 cd/A and 29.6 lm/W, respectively, without out-coupling structure. A low driving voltage of 6.5 V at 1,000 cd/m2 is realized, which is an important value because such a luminance is required for actually employed lighting device. The blue emission appears from 5.4 V, and the light color changes from yellowish to bluish white during 5.4 V to 13.4 V, which could be explained by the energy level structures of the device and proved by the J-V characteristics. Additionally, this tandem WOLED also shows photovoltaic effect. This work provides a design of room light source whose color temperature could be tuned through applied voltage when needed, and a display system for low-current operated amorphous Si-TFT due to its high current efficiency.
Less -
Xiao Li, ... Lian Duan
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0003 - January 13, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards High-Performance and Long-Lifetime OLEDs
Efficient deep-blue fluorescent material serving as emitter and host for high-performance organic light-emitting diodes
-
Blue emitters are highly desired in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), but their electroluminescence efficiencies and roll-offs are always less than satisfactory. In this work, a triazine-based deep-blue emitter (2PhCzTRZ-Cz) is designed and synthesized. ...
MoreBlue emitters are highly desired in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), but their electroluminescence efficiencies and roll-offs are always less than satisfactory. In this work, a triazine-based deep-blue emitter (2PhCzTRZ-Cz) is designed and synthesized. It prefers high thermal stability with a decomposition temperature of up to 543 °C, and possesses strong deep-blue photoluminescence. The doped OLEDs using 2PhCzTRZ-Cz as an emitter attain deep-blue lights at 418-424 nm, with high maximum external quantum efficiencies (ηexts) of 4.46-5.68%, maximum luminances of 2,820-7,400 cd m-2, CIEy values < 0.1 and small efficiency roll-offs. In addition, multiple-resonance thermally activated delayed fluorescence OLED by using 2PhCzTRZ-Cz as host realizes a high maximum ηext of 21.5%, significantly higher than those of the device based on traditional mCBP host (12.9%). These outstanding performances demonstrate the great potential of 2PhCzTRZ-Cz as an emitter and host for OLEDs.
Less -
Ting Guo, ... Zujin Zhao
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0002 - January 09, 2025
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards High-Performance and Long-Lifetime OLEDs
Terphenyl-modified diboron embedded multi-resonance thermally activated delayed fluorescence emitters with high efficiency
-
Nitrogen/boron-based multi-resonance thermally activated delayed fluorescence (MR-TADF) materials offer advantages in terms of high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) and narrowband emission, making them highly promising for display applications. ...
MoreNitrogen/boron-based multi-resonance thermally activated delayed fluorescence (MR-TADF) materials offer advantages in terms of high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) and narrowband emission, making them highly promising for display applications. Represented by ν-DABNA, diboron MR-TADF materials demonstrate the potential for high-efficiency narrowband emission. However, their large planar structures are susceptible to intermolecular interactions, thus increasing the complexity of device fabrication. In this research, our objective was to enhance the anti-aggregation capabilities of the diboron-based ν-DABNA by incorporating sterically hindered terphenyl groups. We synthesized two luminescent materials, DTPF-ν-DABNA and DTP-ν-DABNA, with intermolecular distances exceeding 4 Å in single-crystal stacking, significantly inhibiting intermolecular interactions. Both materials achieved an external quantum efficiency (EQE) exceeding 30% and full width at half maximum (FWHM) of no more than 22 nm, demonstrating characteristics of high-efficiency narrowband emission. Our research provides a straightforward and practical method to obtain MR-TADF materials with high device efficiency and low sensitivity to doping concentration.
Less -
Fu-Ming Liu, ... Zuo-Quan Jiang
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0001 - December 02, 2024
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards High-Performance and Long-Lifetime OLEDs
Triazolotriazine-based thermally activated delayed fluorescence sensitizer for narrowband red fluorescence OLEDs
-
The development of high-performance narrowband red organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) has garnered significant attention, offering both exciting opportunities and formidable challenges. In this study, we report the synthesis of a novel red thermally ...
MoreThe development of high-performance narrowband red organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) has garnered significant attention, offering both exciting opportunities and formidable challenges. In this study, we report the synthesis of a novel red thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) molecule, 10,10',10''-([1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-a][1,3,5]triazine-2,5,7-triyltris(benzene-4,1-diyl))tris(10H-phenoxazine)
Less(TPXZ-TAZTRZ), which integrates a highly electron-deficient triazolotriazine unit as the acceptor and three strongly electron-donating phenoxazine (PXZ) moieties as donors. TPXZ-TAZTRZ exhibits a small singlet-triplet energy gap, enabling a rapid reverse intersystem crossing rate. Additionally, it shows a broad emission spectrum peaking at 634 nm, spanning the yellow-to-red region. These features render TPXZ-TAZTRZ as an ideal TADF sensitizer for narrowband red fluorescent OLEDs. Accordingly, TPXZ-TAZTRZ was employed to sensitize the conventional fluorescent emitter DBP. The resulting TADF-sensitized fluorescence OLEDs (TSF-OLEDs) demonstrated efficient energy transfer from the TADF sensitizer to the emitter, effectively addressing the limitations previous encountered with TADF systems. The devices achievedhigh-performance pure red emission, with Commission International de l'Éclairage (CIE) coordinates of [0.67, 0.33], an emission peak at 612 nm, a narrow full width at half maximum (FWHM) of 27 nm, and a maximum external quantum efficiency of 16.2%. -
Yang Tian, ... Zhengyang Bin
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.70401/smd.2025.0010 - April 22, 2024
-
This article belongs to the Special Issue Towards High-Performance and Long-Lifetime OLEDs